Impact of Digitalisation on the Indian Economy:
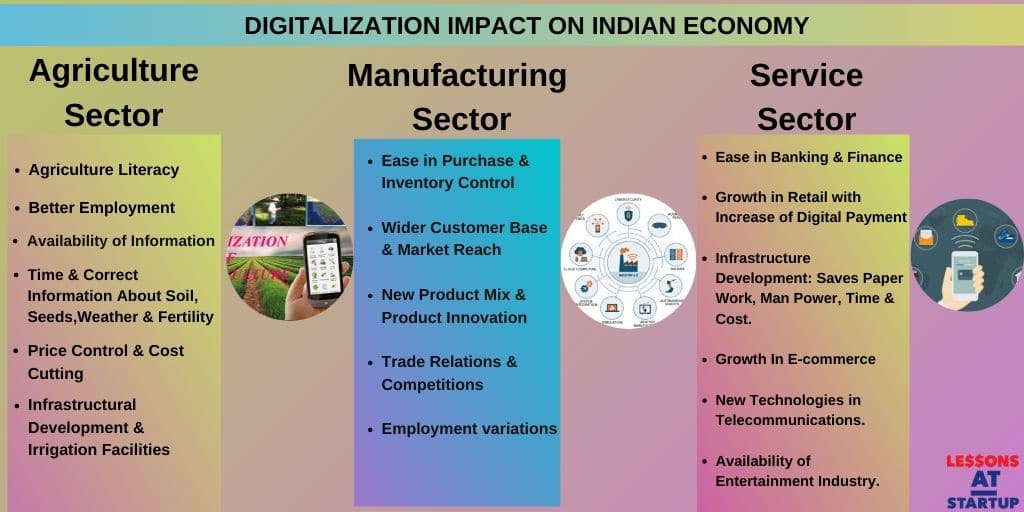
Digitalization has played a vital role in the flourishing of the Indian economy. The most prominent example is the job opportunities created for youth in the country.
In addition to the above, the “make in India” drive has given youngsters an immense push to start new startups and come up with creative ideas to contribute to India’s digitalization.
The government is pushing and encouraging the Indian public to go cashless and reduce their reliance on cash transactions. The purpose is to make us adopt digital payments.
Here are some key examples of how Digitalisation has helped the Indian economy in 2024:
Economic Contribution:
The digital economy is projected to contribute 20% to India’s GDP by 2026 and is expected to reach $1 trillion by 2025
Job Creation:
IT-BPM sector directly employs about 5.1 million people in 2024, with an Indirect job creation estimated at 12-13 million
Digital Payments:
UPI transactions reached 8.7 billion in volume and ₹14.75 trillion in value in January 2023 and it is expected that Digital payments will account for 71.7% of all payments by volume by 20251
Digital Identity:
Over 1.3 billion Aadhaar cards were issued as of 2023.
Digital Documentation:
DigiLocker has more than 145 million users as of 2023
Digital Infrastructure:
BharatNet connected over 1.8 lakh gram panchayats with optical fibre by 2023
E-Governance:
MyGov portal enhances citizen engagement in governance.
ORS (Online Registration System) facilitates online appointments and fee payments for government hospitals.
Financial Inclusion:
Initiatives like Mudra scheme provide unsecured small business loans without collateral.
Transparency and Anti-Corruption:
Digital transactions reduce the circulation of fake currency and curb black money.
Startup Ecosystem:
Digital India and Make in India initiatives boost startup culture and innovation.
Efficiency in Public Services:
Streamlined processes in taxation, banking, and government services reduce bureaucracy.
Digital Literacy:
PMGDisha aims to make 60 million rural households digitally literate1
Emerging Technologies:
National AI Portal showcases AI-related developments in India
Cybersecurity:
Initiatives like Cyber Surakshit Bharat raise awareness about cybercrime
Digital Agriculture:
e-NAM (National Agriculture Market) provides an electronic trading portal for farm produce
These initiatives and their impacts demonstrate digitalisation’s significant role in transforming the Indian economy and enhancing efficiency, transparency, and inclusivity across various sectors.
Since cash is the primary mode of transactions in money laundering and terrorism funding, a digital society would discourage such laundering and terrorism.